UPSC Key: Chicago Convention, Heat Risk Index and Strait of Hormuz
Why grey-list under FATF is relevant to the UPSC exam? What is the significance of topics such as using urban heat island, Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau and flagship schemes for Scheduled Tribes on both the preliminary and main exams? You can learn more by reading the Indian Express UPSC Key for June 18, 2025.
 UPSC Key June 2025: Here's what you should be reading from the June 18, 2025 edition of The Indian Express
UPSC Key June 2025: Here's what you should be reading from the June 18, 2025 edition of The Indian Express
Important topics and their relevance in UPSC CSE exam for June 18, 2025. If you missed the June 17, 2025 UPSC CSE exam key from the Indian Express, read it here
FRONT PAGE
PM to meet leaders at Summit, says will emphasise priorities of the Global South
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Main Examination: General Studies II: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
What’s the ongoing story: Prime Minister Narendra Modi is likely to meet German Chancellor Friedrich Merz, Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and the host, Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney, in Kananaskis where he will also address the G7 leaders’ outreach session.
Key Points to Ponder:
• What is Global South?
• ‘India as the voice of Global South’-Examine
• G7 Summit 2025-know the key highlights
• What are the main points of the G7 Summit?
• What Does the G7 Do?
• Why was the G7 formed, and how does it work?
• What happened with Russia?
• Are there alternatives to the G7?
• How far G7 is effective and influential?
Key Takeaways:
• Modi, who arrived in Canada from Cyprus in the early hours of Tuesday (India time), said in a post on X: “Landed in Calgary, Canada, to take part in the G7 Summit. Will be meeting various leaders at the Summit and sharing my thoughts on important global issues. Will also be emphasising the priorities of the Global South.”
• The Global South includes the developing and the less developed countries of the world.
• This is his first visit to Canada in a decade. Relations between the two countries plummeted in 2023 after Justin Trudeau, the then Canadian Prime Minister, alleged “potential” involvement of Indian government agents in the killing of a Nijjar – a charge India rejected as “absurd” and “motivated”. It led to downgrading of diplomatic ties.
• Modi will be meeting Carney and Merz for the first time as leaders of their countries. All these meetings, including with Meloni and Zelenskyy, are likely to take place between late Tuesday and early Wednesday India time.
Do You Know:
• This is Modi’s first overseas visit after India launched Operation Sindoor on May 7, targeting terror infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir in retaliation for the April 22 Pahalgam terror attack.
• He is on a four-day, three-nation tour to Cyprus, Canada and Croatia.
His presence at the Kananaskis gathering, at the invitation of Prime Minister Carney, marks his sixth consecutive participation at the G7 Summit.
• Randhir Jaiswal, spokesperson for the Ministry of External Affairs, said, the “PM will be participating in G7 discussions on the future of energy security, including diversification, technology, infrastructure and investment, to ensure access and affordability in a changing world.”
• India has attended eleven G7 Summit outreach sessions till date: 2003 (France); 2005 (UK); 2006 (Russia); 2007 (Germany); 2008 (Japan); 2009 (Italy); 2019 (France); 2021 (UK); Germany (2022), Japan (2023), and Italy (2024).
• The G7 is an informal grouping of the world’s advanced economies – France, US, UK, Germany, Japan, Italy and Canada and the European Union. Its members meet annually at the G7 Summit to discuss global economic and geopolitical issues.
• On January 1 this year, Canada assumed the Presidency of the G7, for the seventh time. This year marks the 50th anniversary of the G7 Summit. While India is not a member of the G7, the Prime Minister has attended meetings at previous summits. This will be India’s 12th participation and Modi’s 6th participation in the summit outreach session.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍C Raja Mohan writes on Modi and the G7 summit: Engaging with a divided West
MoD moves to shrink time for procurement, replace trials with simulation
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: General Studies II: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
What’s the ongoing story: Compression of procurement timelines, faster contract awards and quicker payments to private vendors are among specific steps listed by the Ministry of Defence in meetings that it has had with the Finance Ministry in the run-up to and post Operation Sindoor.
Key Points to Ponder:
• ‘The aim of simulation in defence procurement’-what you understand?
• What are defence offsets?
• Under which defence acquisition procedure are simulation-based evaluations being proposed?
• Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020-what you know about the same?
• The DAP 2020 emphasizes ‘Make in India’ by promoting what?
• What are the advantages and limitations of using simulations in defence procurement?
• What are the recent steps taken by the Ministry of Defence to streamline procurement timelines?
• Defence procurement in India has often faced delays due to extensive trial processes-discuss
Key Takeaways:
• Specific measures cited by the Ministry of Defence include the replacement of field evaluation trials, which sometimes take a couple of years or more, with digitisation and simulation to get around long-drawn trials, alongside fast-tracking negotiations to speed up procurement and incentivising the private sector to step up production of vital inputs such as anti-drone equipment and smart ammunition, sources said.
• Officials aware of the discussions said work has been fast-tracked to ensure speeding up procurement deadlines to the end of this year, with special focus on pushing the domestic defence industry, especially private players, and the purchase of equipment that have interoperability between the different services of the armed forces.
• This is linked to specific instructions being issued by the Ministry of Defence to private vendors for upscaling supplies of certain ammunition, including for anti-drone and smart ammunition, alongside equipment such as armored vehicles that can be integrated with different weaponry – loitering munitions and guided missiles.
• The Ministry of Defence has, in the meetings, pitched this as a radically new approach to defence procurement. The Ministry of Finance, in turn, is learnt to have given its explicit support to help meet whatever capex requirement is there from the armed forces, even as it does not see the allocated amount shooting up sharply beyond the allocation in Budget for the ongoing financial year 2025-26, officials said.
• Officials of the Ministry of Defence are learnt to have acknowledged the slow absorptive capacity for capex, especially in terms of the ability to spend the budgeted amount quickly, both in the domestic industry and in terms of global orders because of various geopolitical factors.
• The Defence and Finance ministries have had these discussions in the days before and after Operation Sindoor. They are looking to speed up procurement deadlines to the end of this year. Simulation and digitisation will get around long-drawn field evaluation trials to fast-track the process.
Do You Know:
• As per the latest data by Controller General of Accounts, the Ministry of Defence has spent 9 per cent or Rs 64,221 crore of its overall budget allocation of Rs 6.81 lakh crore in the first month of April of the ongoing financial year. On the capex front, the Ministry has spent 2 per cent or Rs 4,384 crore in April, out of the total budgeted amount of Rs 1.8 lakh crore. In April 2024, the capex had been 1 per cent of the budgeted amount for FY25.
• While experts have pointed out the requirement for India’s defence expenditure to be at least 2 per cent of the GDP for credible deterrence against its neighbouring countries, the defence expenditure has remained below 2.5 per cent over the last five years as a share of the country’s GDP. For FY25 and the ongoing financial year 2025-26, it has been even lower than 2 per cent, estimated to be 1.98 per cent and 1.91 per cent as a share of the GDP, respectively.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Explained: What are defence offsets? Here’ everything you need to know
EXPRESS NETWORK
Centre’s wide outreach aims to push flagship tribal welfare schemes in over 500 districts
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Economic and Social Development
Mains Examination: General Studies II: Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
What’s the ongoing story: The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has rolled out a large-scale outreach campaign for the implementation of its welfare schemes in over 500 districts of the country, aiming to cover 1 lakh tribal dominated villages and habitations.
Key Points to Ponder:
• What you know about Scheduled Tribes (STs)?
• Why they are called as Scheduled Tribes (STs)?
• What are the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment?
• What are the flagship schemes which focuses on the socio-economic development of Scheduled Tribes through area-based development?
• How effective are the Centre’s recent outreach program aimed at implementing tribal welfare schemes in over 500 districts?
• What are the challenges and opportunities associated with delivering welfare schemes in tribal regions of India?
Key Takeaways:
• The outreach has been pegged around ‘benefit saturation’ camps, aimed at doorstep delivery of two key flagship schemes – Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN), launched in 2023, and Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan, which was launched in 2024.
• While PM-JANMAN was launched with a focus on particularly vulnerable tribal groups, the Dharti Aaba scheme was launched as an umbrella initiative aimed at implementation of welfare measures, with the convergence of 17 line ministries. Each line ministry has been allocated budget and targets under the scheme.
• Construction of hostels, rural electrification, building of homes under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, livestock support and fisheries support are some of the welfare benefits being implemented through the Dharti Aaba umbrella scheme.
• The scheme has been named Dharti Aaba (father of the earth) after anti-colonial tribal leader Birsa Munda. Prime Minister Narendra Modi had launched the scheme during the Jharkhand elections last year. In the Union budget, the scheme was allocated Rs 79,156 crore over five years with a central share of Rs 56,333 crore, and state share of Rs 22,823 crore.
• Officially launched on June 15, the outreach campaign will run for a fortnight. Among its focal points are providing basic documentation to tribal communities in the form of Aadhaar cards, Ayushman Bharat cards through enrolment, grant of titles under the Forest Rights Act, and opening of pension accounts as well as Jan Dhan accounts.
• Ministry sources said that one of the key objectives of the outreach programme was last-mile awareness on the flagship JANMAN and Dharti Aaba schemes, down to hamlets and the block level. With an outlay for Dharti Aaba provisioned only in this year’s budget, the Centre hopes to popularise uptake of the scheme through the outreach programme.
• The outreach is also part of the Centre’s ongoing year-long celebration of the Janjatiya Gaurav Varsh. The Centre began this celebration on November 15, 2024, the birth anniversary of Birsa Munda, and the celebrations are a tribute to the contributions of the tribal leader and the tribal community to the freedom struggle.
Do You Know:
Virginius Xaxa writes:
• One of the notable features of the Union Budget 2025-26 is the allocation of funds to the Ministry of Tribal Affairs. At Rs 14,925.81, it is almost a 46 per cent jump from the previous budget. Three crucial initiatives of the ministry — the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN), the Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Utkarsh Abhiyan (DA-JGUA) and the Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS), saw an increase in outlay.
• The PM-JANMAN vision is aimed at improving the socio-economic status of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG) by bridging gaps in health, education, and livelihoods.
• The DA-JGUA scheme is targeted towards saturation coverage of government schemes in health, infrastructure, education, and livelihood. Earlier, the scheme was named Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PM-JUGA). Dharti Aaba (father of the earth) is a title used in Jharkhand to honour Birsa Munda, the anti-colonial tribal leader who fought against British rule in the late 19th century.
• The third important component of the budget is the Eklavya Model Residential School.
• Notably, the tribal sub-plan (TSP) approach was introduced in 1974-75 to address abysmal resource allocation for the ST population. As per the TSP, the budget allocation was to be made in proportion to the size of the tribal population both at the union and state levels. Yet, all through the planned phases, there has hardly been such allocation. Later, the TSP approach was transformed into the Scheduled Tribe Component (STC) and Development Action Plan for Scheduled Tribes (DAPST). In the last 10 years, the budget allocation under the
Development Action Plan for STs (DAPST) has increased manifold.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Experts Explain: How the PM JANMAN scheme can help Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups
Previous year UPSC main Question Covering similar theme:
📍What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)? (2017)
📍Why are the tribals in India referred to as ‘the Scheduled Tribes’? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. (2016)
EXPLAINED
A-I plane crash: What brought overseas safety experts to India?
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
What’s the ongoing story: A 1944 global aviation pact, and the principle of shared air safety, explains the foreign presence at the AI 171 crash site in Ahmedabad.
Key Points to Ponder:
• Why are foreign agencies, particularly from the US and the U.K., involved in investigating the crash of an Indian airline on Indian soil?
• Which international convention governs the investigation of civil aviation accidents?
• What is Chicago Convention, 1944?
• Which article of the Chicago Convention allows the state of aircraft manufacture to participate in crash investigations?
• In the context of aircraft crash investigations, what is the role of the ‘State of Design’?
• What is Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB)?
Key Takeaways:
• The Convention on International Civil Aviation, better known as the Chicago Convention, was signed in 1944 as World War II was drawing to a close. Its framers understood that aviation would connect the world in unprecedented ways, and that ensuring air safety would require shared global responsibility.
• Today, the Convention’s technical standards are overseen by the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO), a UN agency based in Montreal. All 193 member countries—including India, the United States, and the United Kingdom—have agreed to follow its rules. One of the most important of these is Annex 13, which lays out the international protocols for investigating aircraft accidents and serious incidents.
• Chapter 5 of Annex 13 outlines the core responsibilities for conducting such investigations. It clarifies that the goal is not to assign blame or liability, but to improve aviation safety by uncovering causes and preventing future accidents.
Do You Know:
• According to Chapter 5, the responsibility to investigate an aircraft accident lies with the ‘State of Occurrence’ — the country where the accident took place. In addition, other countries connected to the aircraft have a formal right to participate. These include the ‘State of Registry’ (where the aircraft is registered), the ‘State of the Operator’ (which operated the flight), the ‘State of Design’, and the ‘State of Manufacture’ (of the aircraft in question).
• Since the AI 171 air crash occurred on Indian soil, India holds the State of Occurrence right. The investigation into the accident is thus led by the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB), the government agency under India’s Ministry of Civil Aviation responsible for investigating civil aviation accidents and serious incidents.
• The ‘State of the Operator’, which refers to the country where the airline’s principal place of business is located, is also India, as Air India operated the aircraft. The ‘State of Registry’ is India as well; Air India’s Boeing aircraft carry Indian registration markings that begin with VT, following national regulations.
• However, both the ‘State of Design’ and the ‘State of Manufacture’ in this case are the United States. The aircraft was manufactured by Boeing and has engines made by General Electric, both American firms. Thus, US agencies such as the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) are entitled to participate in the investigation, under ICAO Annex 13. The manufacturer, such as Boeing, may also send its own experts as part of the NTSB’s accredited team.
• The UK’s representatives have joined the investigation since 53 British nationals were on board AI 171, all of whom died. All participants in the investigation are entitled to visit the crash site, examine the wreckage and evidence, make technical submissions, and receive the final report.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: General Studies II: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
What’s the ongoing story: Israel and Iran have been attacking each other, and there is no saying how bad the war situation could get. But India’s stock markets have remained calm. The reason: low inflation, a stable macro situation, and limited trade linkages with Iran. Things could change if Israel targets Iranian oil installations
Key Points to Ponder:
• What factors has helped insulate Indian markets from the Iran-Israel conflict?
• India’s crude oil imports are most significantly affected by developments in which regions?
• Why Indian markets have remained relatively unaffected by the Iran-Israel conflict?
• How India’s macroeconomic fundamentals have contributed to market resilience during recent global geopolitical tensions?
• What role do global oil prices play in determining the health of India’s financial markets?
• What are the geopolitical factors that could destabilize Indian markets in the medium to long term, despite short-term resilience?
Key Takeaways:
• On Day 5 of the Middle East conflict, Israel claimed it had killed Iran’s wartime chief of staff, adding to the long list of Tehran’s war casualties, and threatened Ayatollah Ali Khamenei with the same fate as that of Saddam Hussein of Iraq.
• With no end to the hostilities in sight, President Donald Trump advised Iranians to “immediately evacuate” the country’s capital, and later denied having initiated talks with the Islamic Republic for a ceasefire.
• On June 12, a day before Israel first hit Tehran with missiles, the Sensex at the Bombay Stock Exchange closed at 81,691.98. Over the last five days (three trading sessions) the benchmark index has more or less maintained its level — it closed at 81,583 on Tuesday. That’s a loss of just 108 points — 0.13 per cent — since the war broke out.
• According to the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), at the end of 2023, Iran accounted for 12 per cent of global oil reserves, with the world’s third largest proven reserves after Venezuela and Saudi Arabia. Iran also has the second largest reserves of natural gas after Russia.
• Economists and market experts link it to India’s comfortable position in terms of macroeconomics and inflation levels, and to the absence of any significant trade linkages with Iran. Concerns could arise if and when Israel targets Iranian oil installations — which it has not done so far.
• In May, India’s WPI declined to a 14-month low of 0.39 per cent from 0.85 per cent in April. In its monetary policy statement earlier this month, the Reserve Bank of India said that headline inflation based on CPI continued its declining trajectory in March-April and moderated to a near six-year low of 3.2 per cent (y-o-y) in April 2025.
Do You Know:
• A rise in crude prices poses inflationary, fiscal, and external-sector risks for the Indian economy. Crude oil-related products have a share of more than 9% in the WPI basket, and therefore, a 10 per cent increase in crude prices may lead to a 0.9 per cent increase in WPI inflation.
• India imports around 85 per cent of its oil requirement. The share of oil imports in India’s total import bill is more than 25 per cent. An increase in oil prices impacts the current account deficit, which is the difference between the values of goods and services imported and exported.
• A rise in crude oil prices also leads to an increase in the subsidy on LPG and kerosene, pushing up the government’s subsidy bill.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Israel-Iran Conflict LIVE: Khamenei says Iran won’t surrender, warns against US strike
Warmer nights, more humidity: Why 57% of districts face extreme heat risk
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: General issues on Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change – that do not require subject specialization.
Mains Examination: General Studies III: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
What’s the ongoing story: Around 76% of India’s population is currently at high to very high risk from extreme heat, according to a new study. People living in Delhi, Maharashtra, Goa, Kerala, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh face the highest risk from heat in the country, the analysis suggests.
Key Points to Ponder:
• What the study, ‘How Extreme Heat is Impacting India: Assessing District-level Heat Risk’ says?
• What is heat risk index (HRI)?
• What is a heat wave?
• Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) criteria for Heat Waves?
• What is the present situation of Heat Waves in India?
• Why is India facing a prolonged heat wave?
• What is the Impact of these Heat Waves?
• What is an ‘urban heat island’ effect?
• Why are cities hotter than rural areas?
• Analyse the socio-economic and health impacts of extreme heat events.
• Evaluate India’s preparedness in adapting to rising temperatures and extreme heat events.
• Discuss the role of urban planning in mitigating heat stress and ensuring climate resilience.
Key Takeaways:
• The study, ‘How Extreme Heat is Impacting India: Assessing District-level Heat Risk’, was published on May 20. It was carried out by Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) researchers: Shravan Prabhu, Keerthana Anthikat Suresh, Srishti Mandal, Divyanshu Sharma, and Vishwas Chitale.
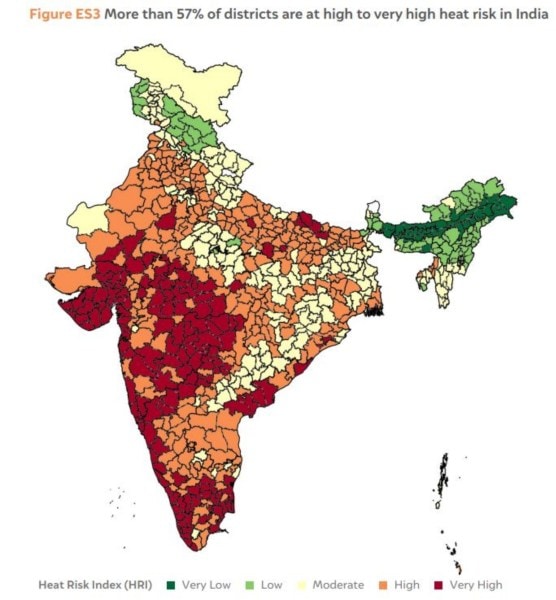 Source: CEEW
Source: CEEW
• For their analysis, the researchers developed a heat risk index (HRI), which assessed heat risk across 734 districts in India. The index is based on 35 indicators, including an increase in frequency of very hot days, population density, percentage of persons with disability, and change in land use and land cover.
Do You Know:
• Contrary to common perception, heat risk is quite different from heat waves and heat stress. While heatwaves — they do not have any universal definition — usually refer to prolonged periods of abnormally high temperatures in a specific region, heat stress is when the body temperature exceeds 37 degrees Celsius in humans and animals. At this temperature, the body is not able to effectively remove excess heat, which can lead to discomfort, heat cramps, and exhaustion. If the body temperature crosses 40 degrees Celsius, a heat stroke can occur.
• Heat risk, on the other hand, is essentially the probability of experiencing heat-related illnesses or death due to exposure to extreme temperatures. It depends on three crucial factors: “the intensity of the heat (and its compounding effects such as humidity); the degree of exposure; and the underlying vulnerabilities of affected communities,” according to the CEEW study.
• The year 2024 was the warmest year on record for the world, including India. While the global average annual mean temperature during the year was more than 1.5 degrees Celsius higher than pre-industrial levels (1850-1900 period), the temperature over India in 2024 was about 1.2 degrees Celsius higher than the 1901-1910 average.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
ECONOMY
Pakistan ‘continues to strengthen’ anti-money laundering system: FATF
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Main Examination: General Studies II: Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
What’s the ongoing story: Pakistan “continues to work with its Financial Action Task Force (FATF)-style regional body, Asia-Pacific Group on Money Laundering (APG), to continue to strengthen its anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing system”, as set out in October 2022, according to the global money laundering and terror financing watchdog.
Key Points to Ponder:
• What is the FATF?
• How many lists are there under Financial Action Task Force (FATF)?
• What is FATF GREY list?
• What FATF’s grey/black lists entail?
• Why Pakistan was on it?
• How grey-list under FATF impacts country?
• Removal of Pakistan from FATF Grey List-how it affected India?
• How India Can Put Pakistan on the FATF Grey List?
Key Takeaways:
• The anti-terror financing body, however, refused to comment on the specific decisions taken against Pakistan in its latest meeting, citing confidentiality, in response to a query sent by The Indian Express.
• On Monday, the FATF in a statement had condemned the “brutal terrorist attack” in Pahalgam on April 22, noting that such attacks cannot occur “without money and the means to move funds between terrorist supporters”.
• When asked whether the FATF has decided to review Pakistan, through consensus of its members, on its compliance with terror investigations, the terror financing watchdog said FATF’s meetings are confidential. “…so we are unable to comment beyond the decisions communicated at the end of last week’s meeting,” it said in its response to this newspaper.
• With the FATF planning to come out with an analysis of terrorist financing — likely to be released in a month — it has compiled cases provided by its global network. The watchdog is learnt to have taken note of ‘state-sponsored terrorism’ in the upcoming report in an oblique reference to Pakistan, sources said.
• Pakistan is also likely to face a review of its legal conviction process linked to terror investigations, sources said. If it happens, this could mean a greater scrutiny of the country’s deficiency in terror case probes that was also flagged at the time of Pakistan’s removal from the FATF’s grey list three years ago.
• When Pakistan was taken off the grey list in October 2022, it was kept in the enhanced follow-up category, following ‘partial compliance’ with a recommendation (R.38) related to deficiency regarding the coverage of predicate offences.
• The recommendation relates to mutual legal assistance (MLA) for freezing and confiscation of proceeds of crime, mainly when crime has happened elsewhere and proceeds are in the relevant country (Pakistan in this case).
Do You Know:
• It requires countries to have authority to take expeditious action in response to requests by other countries to identify, freeze and seize property laundered, proceeds from money laundering or predicate offences. Though Pakistan had issued guidelines for MLA, FATF had noted the deficiencies in its scheme for providing assistance to other countries.
• While the FATF statement on Monday did not name any country, India had earlier stated its intent to take up terror funding charges against Pakistan to make a case for putting it back in the FATF ‘grey list’ in response to the Pahalgam attack in April.
• Twenty-six people were killed in the attack in Jammu and Kashmir’s Pahalgam on April 22. On May 7, India launched Operation Sindoor, striking terror infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which was followed by three days of military confrontation between India and Pakistan.
• The FATF’s statement on Monday came after its plenary meeting last week, where Delhi is learnt to have flagged Pakistan’s terror network and the targeted attacks against India.
• The FATF is the global money-laundering and terror financing watchdog. It is an inter-governmental organisation with 40 members (including Russia whose membership was suspended in 2023).
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍What is the FATF, and why does Pakistan potentially being greylisted matter?
Why Strait of Hormuz is critical for India’s oil and gas imports
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: General Studies II: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
What’s the ongoing story: The global energy market has its eyes set on the ongoing Israel-Iran conflict as the West Asian region is a critical cog in the international oil and gas flows. Indian refiners, too, are watching the developments closely as the region accounts for a significant share of India’s energy imports.
Key Points to Ponder:
• Map Work-Strait of Hormuz
• The Strait of Hormuz connects which two water bodies?
• Why is the Strait of Hormuz strategically important for India?
• Which international law governs freedom of navigation through straits used for international navigation like Hormuz?
• How does the Israel-Iran conflict pose a threat to global oil and gas flows?
• India’s dependency on oil imports through the Strait of Hormuz-know in detail
• What are the potential economic consequences of a conflict-induced blockade of the Strait of Hormuz especially for India?
Key Takeaways:
• Any major disruption in West Asian oil and gas exports could lead to a surge in oil and gas prices in the international market, which would also hurt India, which is counted among the world’s largest oil and gas importers with high import dependency.
• To be sure, the conflict has so far not majorly disrupted physical oil and gas flows from the region, although some inflationary impact on shipping and insurance rates appears to have taken place in the form of higher geopolitical risk premium, industry sources said. There are also reports that a few shipping lines may be reassessing routes, particularly the choke point of the Strait of Hormuz, given the heightened threat in the region. This could further add to the transportation cost to and from the region.
• As for oil prices, benchmark Brent crude jumped 7 per cent on Friday to over $74 per barrel, following Israel’s airstrikes deep inside Iran and the latter’s retaliation. However, despite some energy infrastructure being hit in the conflict over the past few days, oil prices have moderated slightly this week amid reports that Iran was pushing the US—through the Gulf powers—to pressure Israel into a ceasefire. Also, the most critical oil and gas supply infrastructure in the region is reported to be safe and export routes open and functional.
• Energy industry insiders, trade sources, and experts appear largely unanimous in the view that the trajectory oil and gas supplies and prices take hereon amid this conflict would largely depend on whether the critical Strait of Hormuz will continue to be open for marine traffic, and whether oil and gas export infrastructure in the region would remained largely unharmed.
Do You Know:
• Strait of Hormuz is a critical narrow waterway between Iran and Oman, and connects the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea.
• The US Energy Information Administration (EIA) calls it the “world’s most important oil transit chokepoint”, with around one-fifth of global liquid petroleum fuel consumption and global liquefied natural gas (LNG) trade transiting through the strait. Much of India’s oil from key West Asian suppliers like Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE reaches Indian ports via the Strait of Hormuz. A bulk of India’s LNG imports, which come predominantly from Qatar, also come through this vital choke point.
• India is the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil and depends on imports to meet over 85 per cent of its requirement. The country is also among the top importers of LNG, depending on imports to meet around half of its natural gas demand. India’s largest source of crude oil is Russia, followed by West Asian suppliers Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE. India also buys oil from other countries in the region like Kuwait, Qatar, and Oman. Indian refiners do not purchase Iranian crude as Iran’s energy sector is under US sanctions.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
For any queries and feedback, contact priya.shukla@indianexpress.com
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter. Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – IndianExpress UPSC Hub, and follow us on Instagram and X.




- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05























